安阳市网站建设_网站建设公司_数据备份_seo优化
一、计算/设计过程
设计一:用集成运放设计一个输入为0.05v,放大为-100的反相比例运算电路。
对于理想电路,反相比例运算电路的输出电压与输入电压之间的关系如下:![]()
![]() =-100,所以
=-100,所以![]() =100
=100
若是假定R1为100k,则R2=![]() =1k
=1k
为了减小输入级偏置电流引起的运算误差,在同相输入端应接入平衡电阻R3=R1,R4=R2.因此,可以确定R3=R1=100k,R4=R2=1k。
设计二:用集成运放设计一个输入电压为0.1V和0.4V,放大倍数为-10的反相加法运算电路。
对于理想电路,反相加法运算电路的输出电压与输入电压之间的关系如下:![]() ,Ui=Ui1+Ui2当R7=R2时,
,Ui=Ui1+Ui2当R7=R2时,![]() ,Ui=Ui1+Ui2=0.1+0.4=0.5V ,
,Ui=Ui1+Ui2=0.1+0.4=0.5V , ![]() =-100
=-100
所以假设R1为100k时,R2=![]() =10k ,所以R7=R2=10k
=10k ,所以R7=R2=10k ![]() =
=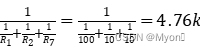
设计三:用集成运放设计一个输入电压为0.1V,输出电压为10.1V同相比例运算电路。
对于理想电路,同相比例运算电路的输出电压与输入电压之间的关系如下:
![]() 和
和![]() =
=![]() =101
=101
所以![]() 假设R1为100k,则R2=
假设R1为100k,则R2=![]() =1k。
=1k。
- 反相比例运算电路
(1) 实验电路图如图2-1-1-1所示
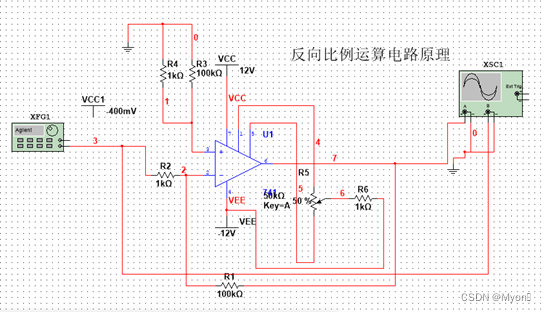
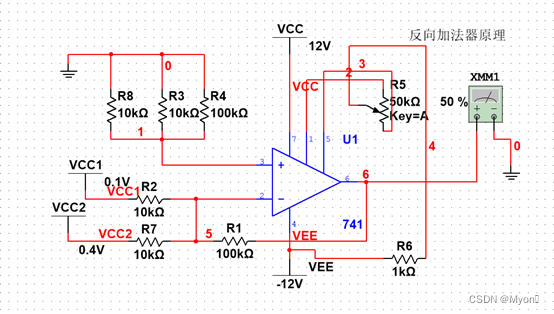
2、反相加法运算电路
(1)实验原理图如图2-1-1-2
3.同相比例运算电路
(1)实验原理图
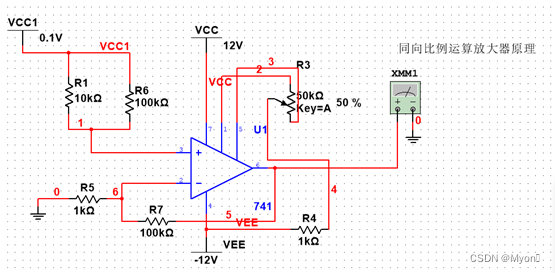
(2)理论计算公式
![]()
![]()
4. 预习计算内容与仿真步骤
(1)预习计算内容
- 根据实验原理,计算预表2-1-1-1、预表2-1-1-2中各项参数(反相比例运算放大)
- 根据实验原理,计算预表2-1-1-3、中各项参数(反相加法器)
