潮州市网站建设_网站建设公司_SSG_seo优化
文章目录
- 目录
- 二叉树
- 1.二叉树的基本概念
- 2.二叉树的应用和时间复杂度
- 3.二叉树的插入
- 4.二叉树的查找
- 5. 二叉树的遍历
- 6.二叉树的删除
- 二叉树的基本操作
- 1.二叉树的基础操作
- 2.代码实现
- 创建二叉树和三种遍历二叉树的方法
目录
- 数据结构:
- 逻辑结构:数组,栈,队列,字符串,树,图
- 存储结构:顺序存储,链式存储
- C++常用的数据结构有:string , stack , queue , deque , vector , list , map , iterators.
二叉树
1.二叉树的基本概念
树是一些节点的集合,节点之间用边链接,节点之间不能有环路。上层的节点称为父节点,下层节点称为子节点。最上层的节点称为根节点。
二叉树是特殊的树。对于每个节点而言,与之直接相连的子节点不能超过两个(可以为0)。左边的子节点称为左子树,右边的子节点称为右子树。如下图就是一颗二叉树:

与树相关的一些概念:
**叶子节点:**没有任何子节点的节点称为叶子节点
深度:对于任意节点N,其深度指的是从根节点到N的唯一路径的长。根的深度为0。深度最深的叶子节点的深度为树的深度。可以理解为:树根是一个入口,离树根越远,就越深。如上图:A、B、C的深度为1,D、E的深度为2。
高: 对于任意节点N,从N到一片树叶的最远路径的长为N的高度。(只可以从从上到下不能经过从下到上的节点。)树叶的高为0。树的高为根的高。如上图,根的高度为2。A的高度为1,其他节点高度为0。
2.二叉树的应用和时间复杂度
二叉树是一种常见的数据结构,常常用于查找,也运用于unix等常见操作系统的文件系统中。c++STL(标准模板库)中的set和map也使用二叉树中的红黑树实现。
- 二叉树的查找思想基于:在二叉树中,对于任意节点N,左子树中的所有项的值不大于节点N中存储的值,右子树中的所有项的值不小于节点N中存储的值。如下图:
这样,在查找时,只需要不断比较需要查找的x与N的大小,若小于N中的值,只需要搜索左子树,若大于N中的值,只需要搜索右子树。这样每次就能缩小搜索的范围。经过证明,普通二叉树的平均时间复杂度是O(LogN)。
看到这里,我们发现其实二叉树的搜索思想和二分查找一致,每次不断的减少搜索范围。但是二者之间还是有区别的。
对于二分查找而言,每次的时间复杂度不会超过O(LogN)。但是对于二叉树,搜索时间的复杂度取决于树的形状。在最坏情况下可能达到O(N)。如下图,如果要找到10,则要查找5次。

那我们为什么还要使用二叉树而不直接使用二分查找来代替?
这是因为,二分查找一般基于数组,如果需要插入或删除数据,则会带来很大的开销。因为每次插入或者删除数据需要将改变节点之后的数据往后挪或者往前挪。但是对于二叉树而言,只需要改变一下指向下一个节点的指针就可以很方便的实现插入或者删除。而且一些特殊的二叉树如红黑树可以保证查找的最坏复杂度不超过O(LogN)。
所以,如果是对于静态数据,不需要改变的数据而言,采用数组存储,使用二分查找比较好。而对于动态数据,需要频繁插入或者删除数据的,采取二叉树存储是较好的。
3.二叉树的插入
思路:插入数据x,从根节点开始,不断比较节点与x的大小。若x小于节点,下一次比较x与节点的左子树,反之,比较x与节点的右子树。直到遇到一个空的节点,插入数据。(我们不考虑插入重复数据) 。如下图:

过程:比较4与7,4<7,再比较4与7的左子树6,4<6,比较4与6的左子树3,4>3,比较4与3的右子树,为空,插入4。
代码:
template< typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::insert(const T &theElement, BinaryNode * &t ) {if ( nullptr == t ){ //如果插入的节点没有创建,则进行创建t = new BinaryNode (theElement);} else if ( theElement < t->element ) { //如果插入的节点小于当前的节点,则继续搜索其左子树insert( theElement, t->leftNode );} else if ( theElement > t->element ) { //如果插入的节点大于当前的节点,则继续搜索其右子树insert ( theElement, t->rightNode );} else {//重复的数据不添加到树中 (找到节点后,直接插入到合适的位置)}
};
4.二叉树的查找
思路:与插入类似,不断比较插入值与节点的值。代码如下
template< typename T>
bool BinaryTree<T>::isFind(const T &theElement, BinaryNode * t ) const {if ( nullptr == t ){return false;} else if ( theElement < t->element ) {return isFind( theElement, t->leftNode );} else if ( theElement > t->element ) {return isFind ( theElement, t->rightNode );} else { //匹配return true;}
};
5. 二叉树的遍历
二叉树的遍历有三种方式:
- 前序遍历(DLR):首先访问根结点。然后如果有子树,则对于左孩子也采用DLR的遍历规则。没有就忽略。然后如果有右子树,则对右子树也采用DRL的遍历规则。没有就忽略。
- 中序遍历(LDR):首先访问根节点的左子树(对左子树也采用LDR),没有则忽略。再访问根节点。最后则对右子树也采用LDR的遍历规则,没有就忽略。
- 后序遍历:首先访问根节点的左子树(对左子树也采用LRD),没有则忽略。再对右子树也采用LRD的遍历规则,没有就忽略。最后则对右子树也采用LRD的遍历规则,没有就忽略。
三种遍历方式其实是根据根节点的访问顺序命名的。根最先方位为前序,次之访问为中序遍历。最后访问为后序遍历。

使用递归实现
前序遍历:
template< typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::preOrder( BinaryNode *bNode ) const {if( nullptr != bNode ) {std::cout << bNode->element << " " ;preOrder(bNode->leftNode);preOrder(bNode->rightNode);}};
中序遍历:
template< typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::inOrder( BinaryNode *bNode ) const {if( nullptr != bNode ) {inOrder(bNode->leftNode);std::cout << bNode->element << " " ;inOrder(bNode->rightNode);}
};
后序遍历:
template< typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::postOrder( BinaryNode *bNode ) const {postOrder(bNode->leftNode);postOrder(bNode->rightNode);std::cout << bNode->element << " " ;
};
6.二叉树的删除



代码
template< typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::remove(const T &theElement, BinaryNode * &t ) {if( nullptr == t ) {return;} else {if ( theElement < t->element) {remove(t->leftNode);} else if ( theElement > t->element ) {remove (t->rightNode);} else if (nullptr != t->leftNode && nullptr != t->rightNode ) { //需要删除的节点两个儿子t->element = findMin(t->rightNode)->element;remove(t->element, t->rightNode);} else {BinaryNode * oldNode = t;t = ( nullptr!= t->leftNode) ? t->leftNode : t->rightNode;delete oldNode;}}
};
emplate< typename T>
typename BinaryTree<T>::BinaryNode * BinaryTree<T>::findMin(BinaryNode *bNode) const {if ( nullptr!= bNode) {while( nullptr != bNode->leftNode) {bNode = bNode->leftNode;}}return bNode;
}
二叉树的完整代码
二叉树的基本操作
1.二叉树的基础操作
- 1.创建二叉树
- 2.递归输出二叉树
- 2.1递归先序输出
- 2.2递归中序输出
- 2.3递归后序输出
- 3.非递归输出
- 3.1非递归先序输出
- 3.2非递归中序输出
- 3.3非递归后序输出
- 4.层次遍历二叉树
- 5.求树高
- 6.求树叶子节点
- 7.按值查找对应节点,输出左孩子结点值和右孩子结点值
- 8.计算所有节点数
2.代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<deque>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;//const int MAX_N = 100;
//数据节点
class Node
{
public:char data;//数据class Node *lchild;//左节点class Node *rchild;//右节点
};//二叉树
class Tree
{
public:Tree(){}~Tree(){}//构建二叉树void Create(string name){ifstream readfile;string str;readfile.open(name);if (readfile.is_open()){getline(readfile, str);//读取一行}readfile.close();CreateNode(str);//构建二叉树}//先序遍历非递归算法void Disp(){if (t == NULL){return;}stack<Node *> m_stack;//定义栈m_stack.push(t);while (!m_stack.empty()){Node *p = m_stack.top();//赋值一份当前双亲节点cout << p->data << ends;m_stack.pop();if (p->rchild)//先存储右子树,确保先输出左子树{m_stack.push(p->rchild);}if (p->lchild)//后存储左子树{m_stack.push(p->lchild);}}}//非递归中序遍历二叉树void DispMid(){if (t == NULL){return;}Node *p = t;stack<Node *>m_stack;while (p != NULL || !m_stack.empty()){while (p != NULL)//一路直走至左下角{m_stack.push(p);p = p->lchild;}if (!m_stack.empty()){p = m_stack.top();//备份当前栈顶地址m_stack.pop();cout << p->data << ends;p = p->rchild;}}}//非递归后序遍历二叉树void DispBehid(){if (t == NULL){return;}Node *pre = NULL, *p = t;stack<Node *>m_stack;while (p != NULL || !m_stack.empty()){while (p != NULL)//一路直走至左下角{m_stack.push(p);p = p->lchild;}p = m_stack.top();//右子树为空或者已访问,输出当前节点if (p->rchild == NULL || p->rchild == pre){cout << p->data << ends;pre = p;//将当前结点地址赋值pre作为下一次判断标志,防止重复访问m_stack.pop();p = NULL;//p赋值空以便访问右子树}else{p = p->rchild;//访问子树的右子树}}}//层次遍历void level_display(){if (t == NULL){return;}deque<Node *>m_qu;//定义队列m_qu.push_back(t);//树根入队列while (!m_qu.empty()){Node *p = m_qu.front();//拷贝当前对头cout <<p->data << ends;//输出m_qu.pop_front();if (p->lchild)//左孩子入队列{m_qu.push_back(p->lchild);}if (p->rchild)//右孩子入队列{m_qu.push_back(p->rchild);}}}//递归先序遍历输出二叉树void display(){cout << "递归先序:";output(t);cout << endl;}//递归中序遍历输出二叉树void displayMid(){cout << "递归中序:";outputMid(t);cout << endl;}//递归后序遍历输出二叉树void displayBhind(){cout << "递归后序";outputBhind(t);cout << endl;}//二叉树高度void Height(){int height = get_height(t);cout << "Height: " << height << endl;}//输出叶子节点值void display_leaf(){cout << "Leaves: ";output_leaf(t);cout << endl;}//查找二叉树中值data域为elem的节点void find_node(char elem){Node *res = NULL;res = find_node(t, elem, res);if (res != NULL){cout << "nice." << endl;if (res->lchild){cout << "left child:";cout << leftchild(res)->data << endl;}if (res->rchild){cout << "right child:";cout << rightchild(res)->data << endl;}}else{cout << "NO." << endl;}}//计算节点数void nodes_count(){int sum;if (t == NULL)//若为空,则0个节点{sum = 0;}else{sum = node_count(t);cout << "Total Nodes:" << sum + 1 << endl;}}
private:Node *t;//构建二叉树void CreateNode(string str){stack<Node *> m_stack;Node *p;int k;while (str.length() != 0){//若当前为'(',将双亲节点推入栈,下一位存储的p值作为左节点处理if (str[0] == '('){m_stack.push(p); k = 1;}//为右括号则栈顶退出一位else if (str[0] == ')'){m_stack.pop();}//为',',则下一个字符作右节点处理else if (str[0] == ','){k = 2;}//存储值用作双亲结点else{p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = str[0];p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;//树根为空时,将第一个节点作为树根并赋值给私有成员变量if (t == NULL){t = p;}//树根不为空else{if (k == 1)//作为左节点处理,将栈中双亲节点的左指针指向当前节点{m_stack.top()->lchild = p;}else//作为右节点处理{m_stack.top()->rchild = p;}}}//重构串,除去首字符,并将串长度减小1str.assign(str.substr(1, str.length() - 1));}}//递归先序遍历输出二叉树void output(Node *t){if (t != NULL)//当树根不为空时{cout << t->data;//输出if (t->lchild != NULL || t->rchild != NULL)//左/右结点不为空时递归到下一层{cout << "(";output(t->lchild);if (t->rchild != NULL)//当左节点遍历结束后,左节点递归返回一层,递归右节点{cout << ",";}output(t->rchild);cout << ")";}}}//递归中序遍历二叉树void outputMid(Node *t){if (t == NULL)//空则返回{return;}else{cout << "(";outputMid(t->lchild);//递归左孩子节点if (t->rchild != NULL){cout << ",";}cout << t->data;//输出outputMid(t->rchild);//递归右孩子结点cout << ")";}}//递归后序遍历输出二叉树void outputBhind(Node *t){if (!t)//空则返回{return;}else{cout << "(";outputBhind(t->lchild);//递归左孩子节点if (t->rchild != NULL){cout << ",";}outputBhind(t->rchild);//递归右孩子结点cout << t->data;//输出cout << ")";}}//求树高int get_height(Node *t){int leftheight, rightheight;if (t == NULL)//递归至不存在子节点时返回0{return 0;}else{leftheight = get_height(t->lchild);//递归求左子树高度rightheight = get_height(t->rchild);//递归其右子树高度return leftheight > rightheight ? leftheight+1 : rightheight+1;//递归返回时返回最大值}}//查找左节点Node *leftchild(Node *p){return p->lchild;}//查找右节点Node *rightchild(Node *p){return p->rchild;}//输出叶子节点void output_leaf(Node *t){if (t != NULL)//树根不为空时{//当前节点没有子节点时输出节点数据if (t->lchild == NULL&&t->rchild == NULL){cout << t->data << ends;}output_leaf(t->lchild);//递归左子树output_leaf(t->rchild);//递归右子树}}//查找二叉树中值data域为elem的节点Node * find_node(Node *t, char elem, Node *res = NULL){//Node *res = NULL;if (t == NULL)//若当前节点为空,则返回结束{return NULL;}else{if (t->data == elem)//若找到值,返回地址{//res = t;return t;}else{if (res == NULL)//若保存结果的指针不为空,则递归查找左节点{res = find_node(t->lchild, elem, res);}if (res == NULL)//若保存结果的指针不为空,且左节点为搜索到,则递归查找右节点{res = find_node(t->rchild, elem, res);}}return res;}}//计算节点数int node_count(Node *t){int lcount = 0, rcount = 0;if (t == NULL)//空则返回{return 0;}else{if (t->lchild != NULL)//遍历左孩子节点{lcount = node_count(t->lchild);lcount += 1;}if (t->rchild != NULL)//遍历右孩子节点{rcount = node_count(t->rchild);rcount += 1;}return lcount + rcount;//返回当前左右孩子节点数}}
};int main()
{Tree m_tree;m_tree.Create("data");m_tree.display();//递归先序输出m_tree.displayMid();//递归中序输出m_tree.displayBhind();//递归后序输出m_tree.Height();//树高m_tree.display_leaf();//叶子节点cout << "非递归先序:";//cout << "Fir:";m_tree.Disp();//非递归先序遍历cout << endl;cout << "非递归中序:";//cout << "Mid:";m_tree.DispMid();//非递归中序遍历cout << endl;cout << "非递归后序:";//cout << "Bac:";m_tree.DispBehid();//非递归后序遍历cout << endl;cout << "层次遍历:";m_tree.level_display();//层次遍历cout << endl;cout << "Input element:";char elem;cin >> elem;m_tree.find_node(elem);//按节点值查找m_tree.nodes_count();//计算节点数return 0;
}

创建二叉树和三种遍历二叉树的方法
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string.h>using namespace std; //定义二叉树的结构体
typedef struct BTree{int val;struct BTree *left , *right;
}BTree; //二叉树类的实现
class Tree{
public:Tree();~Tree();//其他操作方法BTree *create_node(int level,string pos); void PreOrder(BTree *t); //先序遍历 void InOrder(BTree *t); //中序遍历 void PostOrder(BTree *t); //后序遍历BTree* root; //定义根节点
};BTree* Tree::create_node(int level,string pos){int data;BTree *node = new BTree;cout<<"please enter data:level"<<level<<" "<<pos<<endl;cin>>data;//若输入的数据为0,则把该结点的子结点置为空 if(data == 0) { return NULL; } node->val= data; /*create_node()的 参数用于在给二叉树赋值时表明 现在赋值的是哪个结点*/ node->left = create_node(level+1,"left"); node->right= create_node(level+1,"right"); return node;
}void Tree::PreOrder(BTree *t)
{ if(t) { cout<<t->val<<endl;; PreOrder(t->left); PreOrder(t->right); }
} void Tree::InOrder(BTree *t)
{ if(t) { InOrder(t->left); cout<<t->val<<endl;; InOrder(t->right); }
} void Tree::PostOrder(BTree *t)
{ if(t) { PostOrder(t->left); PostOrder(t->right); cout<<t->val<<endl; }
} int main()
{ Tree tree; tree.root = tree.create_node(1,"root"); cout<<"Pre"<<endl; tree.PreOrder(tree.root); cout<<"In"<<endl; tree.InOrder(tree.root); cout<<"Post"<<endl; tree.PreOrder(tree.root); return 0;
}
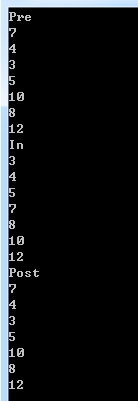
输入:
7
4 10
3 5 8 12
输出: